Lab-Grown Diamonds’ Journey from 1954 to Today-HISTORY OF LAB GROWN DIAMONDS
The history of lab grown diamonds dates back to the mid-20th century when scientists first embarked on the quest to create synthetic diamonds that possess the same physical and chemical properties as natural diamonds. The lab grown diamond is made under controlled temperatures and the environment in the laboratories using advanced technologies and types of equipment. They are similar to natural diamonds in terms of optical, chemical, and physical properties.
How is lab grown diamond made?
Diamonds made in laboratories are processed maintaining similar environmental conditions in which natural diamonds are required to form. Natural diamonds take several millions of years to form and are then mined from within the earth, but lab created diamonds are created in laboratories keeping similar conditions intact.
Natural diamonds undergo high pressure and are exposed to hot temperatures, after which the diamonds are formed naturally under the earth’s crust after millions of years. Similarly, lab made diamonds are also exposed to high pressure and high temperatures in the laboratories, and then they get formed.
Conditions remain identical for the creation of both naturally mined diamonds and lab grown diamonds. Therefore, due to similar conditions and temperatures being exposed, these diamonds resemble the same chemical structure and also have identical optical, and physical properties and features which mined diamonds possess.
History of Lab Grown Diamonds
Creation of the very first diamond in the laboratory
There have been a few claims that state that diamonds made in the lab were manufactured between the year 1879 to 1928 by researchers. However, no such claim has been confirmed or approved by any Federation as of now.
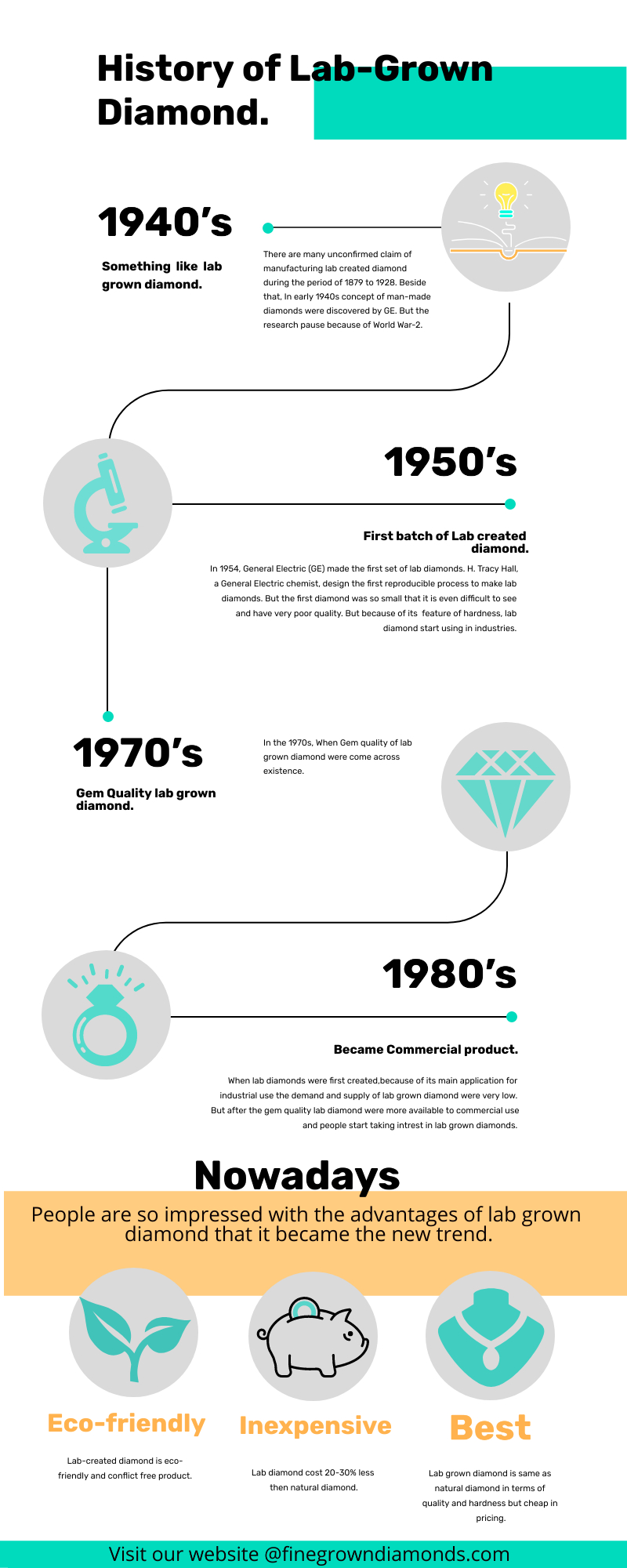
According to specific resources, it is known that diamonds created in a lab or man-made diamonds in the laboratory has been in existence since the year of early 1940s. The very first batch of lab diamonds was made by General Electric (GE) in the year 1954. Gradually in the year 1970s, further manufacturing of gem-quality stones started being made in the laboratories.
When did the lab diamonds come into commercial use?
During all these years, lab made diamonds were being created but were not available for commercial use in the market. The lab grown diamonds started being made accessible for commercial use only in the year 1980s and were made in high and premium Quality for commercial purposes. The processes used in making the diamonds in the laboratory have, however relatively improved only in the last decade.
The processes which are being used in the creation of human-made diamonds have seen tremendous improvement. Because of such improvisations, the lab grown diamonds can now possibly be used in various jewelry and also in the manufacturing of engagement rings containing diamonds.
Where and by whom was the first batch of diamonds made in the laboratory?
General Electric (GE) created the very first batch of diamonds in the lab in the year 1954. They had started with this research related to manufacturing diamonds in the laboratory a lot of years before it was first made. The research began in the year 1941. They made a team that consisted of researchers and developers to work on this revolutionary technology in the endeavor to create diamonds in lab and make it a successful one.
However, they had to put a pause to research midway due to the commencement of the Second World War during that time. Once the Second World War was done with, they further continued with research and development team and started working towards creating man-made diamonds.
There were other groups as well who worked on creating lab grown diamond. Swedish Electrical Utility (ASEA) had also created diamonds in the laboratory but did not reveal them. They kept this discovery of theirs a secret until the year of 1980s and opened up about it thereby. This helped General Electric (GE) in being able to become the first one to create the first set of diamonds in the lab.
Who invented the process of creating diamonds in the laboratory?
Tracy Hall, who was a General Electric chemist, was the first person to have discovered the very first reproducible process which helped in the making of lab created diamonds. He made the discovery of the process in the early years of the 1950s. Creating the process to make diamonds in the laboratory was one of the chief aims of a lot of people in history which including chemists, physicists, alchemists and many other parties as all were interested for many centuries.
The first diamond which was manufactured in the laboratory manually was very tiny and small. It was also of inferior and degraded Quality. Due to being excessively small in size, it was almost invisible to the naked eye. They were only suitable for being used in the industries.
However, the Quality and size of man-made diamonds have evolved since and have now become of premium quality that it almost difficult to be able to distinguish between a naturally mined diamond and a lab-made diamond.
Availability of lab diamonds in varying Quality and sizes
Over the years, advanced technologies and improved methods of production of lab made diamonds have relatively facilitated its Quality. It has improvised the manufacturing of lab grown diamonds up to twelve carats. These lab diamonds which are available in 12 carats can now be studded in engagement rings to give a stunning and classy look to the wearer. Not only size but also the Quality of lab made diamonds has become much better with time. Since the first creation of lab created diamonds, until today, there has been a considerable improvement in these diamonds.
Anyone can now avail of diamonds in a wide variety of premium quality ranges. They have varying clarity, cuts, and color, which are similar to mined diamonds. One can choose which size, color, clarity, cut, and Quality they wish to purchase. All are available at differing prices and are much more affordable than natural diamonds since the mining costs get deducted for the lab diamonds.